Recommended VirtualBox Version for use with Whonix

This wiki page provides information on the recommended version of VirtualBox for use with Whonix, along with installation instructions.
It is strongly advised to use the recommended VirtualBox version with Whonix, otherwise there can be issues. [1]
Download and install VirtualBox for your operating system.
Windows
Microsoft Visual C++ 2019 Redistributable Package
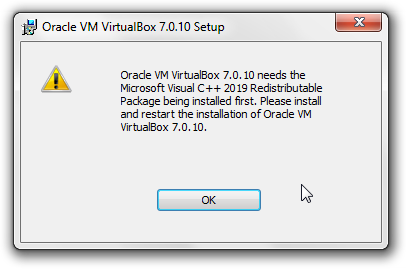
If you see the following error message:
Figure: Microsoft Visual C++ 2019 Redistributable Package Error
Oracle VM VirtualBox needs Microsoft Visual C++ 2019 Redistributable package installed first. Please install and restart the installation of Oracle VM VirtualBox.
Microsoft Visual C++ 2019 Redistributable Package must be installed. [2]
Optional: Digital signature verification.
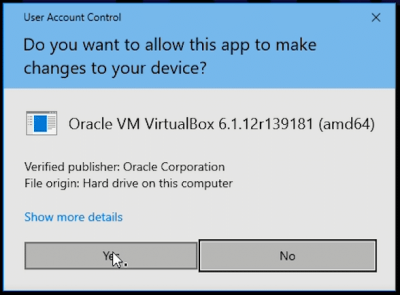
VirtualBox for Windows is not signed with OpenPGP / gpg. It is signed with authenticode.
After downloading the VirtualBox installer exe and starting it, the user should verify that sure that Verified publisher: is Oracle Corporation.
Figure: Windows signature signature verification window for VirtualBox
Advanced users might wish to learn more about Authenticode (Windows Digital Software Signatures)![]() to perform a deeper verification.
to perform a deeper verification.
macOS
Select your hardware platform.
Optional: Digital signature verification.
VirtualBox for macOS is not signed with OpenPGP / gpg. It is notarized for macOS's gatekeeper.
See also Apple's official documentation Safely open apps on your Mac![]()
.
Ubuntu
For Ubuntu host operating systems
Choose an option from the following table. Choose either Option (A) OR Option (B).
A Automated VirtualBox Installation : Ubuntu users could alternatively use the Whonix Linux Installer for VirtualBox. In this case, this wiki page can be completely ignored. No other steps from this wiki page need to be applied because the automated installer will handle everything.
B Manual VirtualBox Installation : Follow the instructions below.
Tested on October 2022 using Ubuntu version 22.04. Older versions are not recommended.
Command Line (All Users)
1 On the host : Open a terminal.
2 Update the package lists.
sudo apt update
3 Install VirtualBox and Linux kernel headers.
sudo apt install --no-install-recommends virtualbox-qt linux-headers-generic
4 Add your current user to group vboxusers. [3]
sudo adduser $(whoami) vboxusers
5 Prevent KVM from conflicting with VirtualBox.
This is necessary if your system uses Linux 6.12 or higher.
echo 'options kvm enable_virt_at_load=0' | sudo tee /etc/modprobe.d/disable-kvm-virt-at-load.conf
6 Reboot.
To ensure KVM configuration takes effect.
7 Done.
The procedure of installing the VirtualBox host software is complete.
Software Center (only if not using SecureBoot)
Ubuntu Software Center can be used to install VirtualBox. The process is similar to installation of most other applications.
This only works for users with computers that do not have " Secure Boot![]() " enabled. If the user's computer is using "SecureBoot" the user need to either disable "SecureBoot" in the BIOS or use the command line based instructions. [4]
" enabled. If the user's computer is using "SecureBoot" the user need to either disable "SecureBoot" in the BIOS or use the command line based instructions. [4]
1 Open the start menu.
2 Click on the Ubuntu Software Center icon.
Figure: Ubuntu Software Center icon
3 Click on the magnifying glass to search. → Type virtualbox. → Press enter. → In the search results, click on VirtualBox.
Figure: Ubuntu Software Center - Search For VirtualBox
4 Click on Install and wait.
Figure: Ubuntu Software Center Search Result
5 Installation of VirtualBox has been completed.
When the installation has completed, the install icon changes to the uninstall icon. Do not click the uninstall button.
Figure: Ubuntu Software Center - VirtualBox has been installed
6 Click on Show Applications. → Click on Virtual Box start the VirtualBox graphical user interface (GUI).
Figure: Ubuntu Software Center #4
7 Prevent KVM from conflicting with VirtualBox.
This is necessary if your system uses Linux 6.12 or higher.
echo 'options kvm enable_virt_at_load=0' | sudo tee /etc/modprobe.d/disable-kvm-virt-at-load.conf
8 Reboot.
To ensure KVM configuration takes effect.
9 Done.
The procedure of installing and starting VirtualBox is complete.
Debian
For Debian host operating systems Choose an option from the following table. Choose either Option (A) OR Option (B).
A Automated VirtualBox Installation : Debian users could alternatively use the Whonix Linux Installer for VirtualBox. In this case, this wiki page can be completely ignored. No other steps from this wiki page need to be applied because the automated installer will handle everything.
B Manual VirtualBox Installation : Follow the instructions below.
Select your Debian release below to get the matching instructions.
Debian Bookworm (oldstable) or Bullseye (oldoldstable)
To acquire the Recommended VirtualBox version tested with Whonix, package virtualbox-qt should be installed from Debian fasttrack repository![]()
according to the following instructions. [5]
1 On the host : Open a terminal.
2 Update the package lists.
sudo apt update
3 Install the Debian fasttrack signing key.
sudo apt install --no-install-recommends fasttrack-archive-keyring
4 Add the Debian fasttrack repository.
echo 'Types: deb URIs: https://fasttrack.debian.net/debian/ Suites: trixie-fasttrack Components: main contrib non-free Enabled: yes Signed-By: /usr/share/keyrings/fasttrack-archive-keyring.gpg' | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/fasttrack.sources
5 Add Debian the backports repository. [6]
echo 'Types: deb URIs: https://deb.debian.org/debian Suites: trixie-backports Components: main contrib non-free Enabled: yes Signed-By: /usr/share/keyrings/debian-archive-keyring.gpg' | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/backports.sources
6 Update the package lists again. [7]
sudo apt update
7 Install VirtualBox and Linux kernel headers.
sudo apt install --no-install-recommends virtualbox-qt linux-headers-$(dpkg --print-architecture)
8 Add your current user to group vboxusers. [3]
sudo adduser $(whoami) vboxusers
9 Done.
The procedure of installing the VirtualBox host software is complete.
Debian trixie (stable) or Testing
Debian Unstable
VirtualBox can be installed by adding the Debian unstable (sid) repository.
1. Update your package lists.
sudo apt update
2. Install VirtualBox and Linux headers, which are a dependency.
sudo apt install --no-install-recommends virtualbox-qt linux-headers-$(dpkg --print-architecture)
3. Add your Linux user account go Linux user group vboxusers.
sudo adduser $(whoami) vboxusers
The details of this are unspecific to Whonix and undocumented.
Other Debian Releases
Other Debian releases might work, but this is untested. In case of other Debian release:
Kicksecure
Kicksecure™ host operating systems
Choose an option from the following table. Choose either Option (A) OR Option (B).
A Automated VirtualBox Installation : Kicksecure™ users could alternatively use the Whonix Linux Installer for VirtualBox. In this case, this wiki page can be completely ignored. No other steps from this wiki page need to be applied because the automated installer will handle everything.
B Manual VirtualBox Installation : Follow the instructions below.
Linux
Hosts using a non-Debian operating system:
- Install VirtualBox as per the normal mechanism for your Linux distribution. No special instructions for Whonix are required. The installation of a recent VirtualBox host software is unspecific to Whonix. Consult the documentation of your Linux distribution.
- You may need to disable KVM's "enable virt at load" feature if your system uses kernel 6.12 or later. This will prevent KVM from taking over virtualization-related features on the system automatically. This will not prevent KVM virtual machines from being used. Add
kvm.enable_virt_on_load=0to your system's kernel command line, or addoptions kvm enable_virt_at_load=0to your system's modprobe configuration, using the appropriate mechanism for your distribution. - Whonix has has been tested with, expects VirtualBox version
latest. - For example the outdated VirtualBox version
5.2.18is incompatible.
Latest VirtualBox Version
[edit]How to find out what the latest VirtualBox version is?
The latest version of VirtualBox can be seen on virtualbox.org/wiki/Downloads![]()
, virtualbox.org/wiki/News
![]()
and VirtualBox announcements newsletter archive
![]()
.
Alternatively the version number can be seen on the VirtualBox Wikipedia page![]()
, although there might be times when Wikipedia is outdated.
The user could also consider to subscribe to the VirtualBox announcements newsletter![]()
.
See Also
[edit]- Stable Whonix Version for VirtualBox
- Whonix for VirtualBox - Testers Only Version
- Install Newer Versions of VirtualBox
- VirtualBox Guest Additions and Shared Folders
- VirtualBox Troubleshooting
Footnotes
[edit]- ↑
- Newer VirtualBox versions not listed on this wiki page or otherwise in Whonix News are untested by Whonix developers.
- This can cause issues such as:
- instability (VirtualBox VMs not starting

),
- VMs suddenly closing,
- host freezing,
- VM black screen.
- instability (VirtualBox VMs not starting
- This can cause issues such as:
- It is therefore advised to wait until newer versions of VirtualBox are recommended for use with Whonix.
trixieand Ubuntu, are at times difficult to install.- For some Linux distributions, the VirtualBox host software is available (for example, as a Debian package) from the
virtualbox.orgrepository, but VirtualBox guest additions are generally unavailable in package format from thevirtualbox.orgrepository.- Using an older version of VirtualBox guest additions (like the pre-installed ones) might lead to broken functionality such as an inability to resize the VM or general instability.
- Installation of VirtualBox guest additions from ISO might also cause issues.

- VirtualBox Unavailable in Debian stable and backports due to Debian Stable Security Maintenance Issues
- Debian VirtualBox feature request: upload to Debian fasttrack

- Debian fasttrack feature request: please add VirtualBox to fasttrack

- Missing dependencies on Buster for Virtualbox 6.1.6

- VirtualBox feature request: Guest Additions Debian Packages unavailable from Oracle Repository

- building VirtualBox from source code failing and nobody could fix it

, and again

.
- Debian's
checkbackport
stating

that creating a backport from the Debian
sidVirtualBox source package is not possible. - Installing VirtualBox on Debian 10 / Debian buster / buster-backports / fasttrack

- Call for help:
- VirtualBox Integration
- Challenges Installing VirtualBox

- Newer VirtualBox versions not listed on this wiki page or otherwise in Whonix News are untested by Whonix developers.
- ↑
This link has been found on the
microsoft.comwebsite: Microsoft Visual C++ Redistributable latest supported downloads
- ↑ 3.0 3.1
Optional: See: https://www.virtualbox.org/manual/ch02.html#install-linux-vboxusers

Also spams
~/.config/VirtualBox/VBoxSVC.loglog if not done. - ↑
This is unspecific to Whonix. This is because during package installation of a package that requires kernel modules when "SecureBoot" is enabled, Ubuntu's
dkmsis prompting the user for a password to encrypt the key which will be used to enroll the kernel module signing key. This is Ubuntu usability issue. It is unknown if any bug report / feature request for this exists. Please contribute, research, report this issue on Ubuntu's issue tracker. - ↑
This is non-ideal
 but required since VirtualBox in unavailable in official Debian
but required since VirtualBox in unavailable in official Debian trixierepository and difficult to install due to VirtualBox Installation Challenges. Alternatively you could install VirtualBox from the Oracle (virtualbox.org) Repository, but this comes with different risks. VirtualBox might be updated by VirtualBox developers before being tested with Whonix which could then lead to issues. (Described in footnote Recommended Version.) - ↑
This is required because the Debian
fasttrackrepository depends on the Debianbackportsrepository. - ↑
This is to acquire the Debian
fasttrackrepository package sources. - ↑
https://www.virtualbox.org/ticket/17055#comment:3


We believe security software like Whonix needs to remain open source and independent. Would you help sustain and grow the project? Learn more about our 13 year success story and maybe DONATE!